Perimeter Intrusion Detection
Perimeter Intrusion Detection
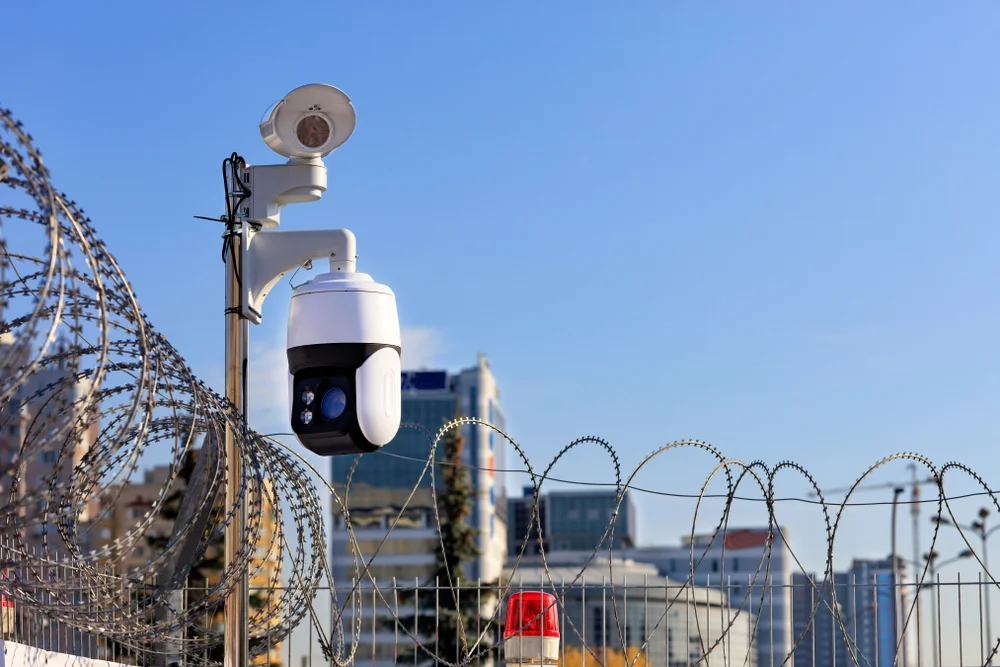
• A Perimeter Intrusion Detection System (PIDS) is a security solution designed to detect the presence of an intruder attempting to breach the physical boundary or perimeter of a protected property, facility, or secure area.
• PIDS acts as the first line of defense, providing an early warning that allows security personnel to respond before the intruder can gain access to critical assets, buildings, or internal zones.
Key Components and Function
• PIDS combines various technologies to create a comprehensive and reliable security layer.
1. Detection Sensors: These are the core components that generate an alert when the perimeter is disturbed.
2. Central Control Unit/Processor: This unit receives signals from the sensors, analyzes the data to filter out environmental noise (like wind or small animals), and determines if a true alarm condition exists.
3. Alarm and Integration System: The processor triggers a response, such as :
• Sending an alert to a central monitoring station.
• Activating deterrents (e.g., lights, sirens).
• Integrating with CCTV to automatically direct a camera to the alarm location for visual verification.
Common Detection Technologies
1. PIDS technologies are generally categorized based on where the sensor is placed: on a fence, in an open area, or buried underground.
2. Fence-Mounted SensorsAttached directly to the fence fabric or support posts.Detects vibration (from climbing or cutting), tension (from lifting the fence), or acoustic signatures. Often uses fiber optic cable or specialized microphonic cable.Facilities with existing physical fences (military bases, industrial sites).
3. Active Infrared (IR) BeamsPosts placed at intervals to create an invisible beam path.An alarm triggers if a continuous beam of invisible IR light is broken by a person or object crossing the area between the transmitter and receiver.Gates, walls, or open, flat stretches where a clear line of sight is available.
4. Microwave/Radar BarriersTransmitter and receiver units placed at distances to create a three-dimensional detection field.Uses radio waves (microwave) or pulsed signals (radar) to detect movement within the zone.Large, open areas or complex terrain where IR beams are impractical.
5. Buried SensorsPlaced underground, either near the fence line or across an open field.Detects seismic or pressure changes in the soil caused by footsteps, vehicles, or digging attempts.High-security or covert applications where visual detection is not desired (e.g., borders).
6. Video AnalyticsUsed with standard or thermal CCTV cameras.AI algorithms analyze the video feed in real-time to identify suspicious actions (loitering, climbing, entering a restricted zone) and distinguish human activity from environmental factors.As a primary system or for alarm verification in almost any application.
• The most effective PIDS installations often use a layered security approach, combining two or more complementary technologies to maximize detection accuracy and minimize false alarms.